with Playchat & MS Azure STT
- PlaychatView.xaml
- PlaychatViewModel.cs
This menu is an example of a Conversational AI service that integrates AI Human, PlayChat and Microsoft Azure STT. Basically, AI Human and Playchat are in the form of chatting by the user inputting with the keyboard. Additionally, use Azure STT to speak like a real person. When the AI load is complete, the AI greets you. ("Hello, long time no see.")
After the greeting, chat or click the STT button at the bottom to get a voice input signal, say "where are you". (Actual operation is possible after the Azure STT setup is completed. It is explained below in this chapter.) The AI understands the voice and the AI gives an appropriate answer. Currently, as it is a test chatbot, it can answer only a few limited questions, but if the chatbot is advanced, it can be used in various ways, such as ordering at a restaurant or making a reservation for a performance depending on the situation. In addition, the chatbot can also display images by sending additional information in addition to text.
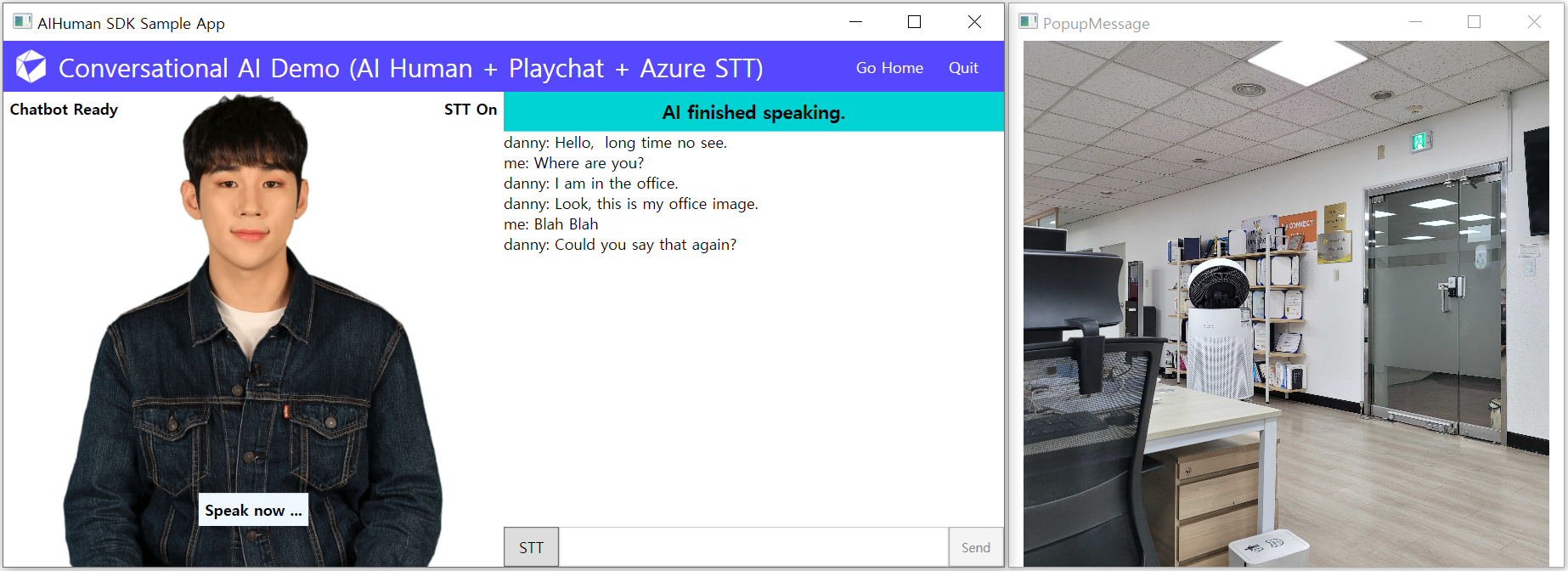
Using AI Human, Chatbot and MS Azure Speech Recognition
If you want to use the conversational AI service mentioned in the demo, you need to prepare as follows.
- Prepare your Playchat Bot ID: Already prepared in the sample (https://www.playchat.ai/docs/en/menual-chatbot-en.html)
- Prepare Azure Speech Service Key and Endpoint: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cognitive-services/speech-service/overview
Assign values to the PLAYCHAT_BOT_ID, AZURE_STT_URL, and AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY variables declared at the top of the class definition of the PlaychatViewModel.cs file.
The main thing is to continue the conversation with AI and voice. For this, AIPlayer, chatbot, and voice recognition must work harmoniously. The class that implements this is PlaychatViewModel.
First, after the chatbot is loaded, it sends a "start"(Constants.KEY_START) signal to the chatbot, and when the chatbot recognizes it, it sends a greeting message. The greeting is delivered via IChatbotCallback's OnChatbotMessage function. PlaychatViewModel extracts the sentences to be delivered to AI from this message and delivers them to AIPlayer, allowing AI to speak.
public void OnChattingReady()
{
SendMsgToChatbotAndUpdateChatUI(Constants.KEY_START, null);
}
public void OnChatbotMessage(JObject response)
{
OnNewChatMessage(response);
if (response != null)
{
// get func_name, args
string fName = response.GetValue(Constants.KEY_FUNC_NAME).ToString();
JObject args = response.GetValue(Constants.KEY_ARGS).ToObject<JObject>();
// process for functions accordingly
ProcessOnNewFunc(fName, args);
}
}
Data transfer format of Chatbot (Playchat)
When speech is recognized through Azure STT, the content is delivered directly to the Playchat server. However, there are situations where you need to manually send a message or special signal to the chatbot. (This includes the "start" signal mentioned above.) To send the user's message, use the chatbot's Send function.
bool Send(string command, JObject detail)
Write the server function name you want in the command, and put the necessary arguments as key:value in detail. The currently set command (or func_name, the same) is as follows.
namespace AIHuman.Common.Constants
{
// send
public const string VALUE_USERINPUT_FUNCNAME = "userInput";
public const string KEY_START = "start";
// recv
public const string VALUE_FUNCNAME_ONMESSAGE = "onMessage";
// extra
public const string VALUE_USERINPUT_NEXT = ":next";
}
In the userInput function, input the argument value with text as the key.
start function takes no arguments.
OnMessage basically comes with the following values. In particular, if the next value is true for 'extra' here, it means that there are additional messages.
/* example
{"func_name":"onMessage",
"args":
{"kind":"Content",
"text":"Hello, long time no see.",
"languages":{"en":"Hello, long time no see."},
"image":{"url":"http://...,"displayname":"office image.jpg"}
"extra":{next:true}}}
*/
- If there is an additional message, you can receive the additional message by sending it by adding ":next" (VALUE_USERINPUT_NEXT), which is a special argument indication, as the argument text in userInput.
private void RequestNextMessageIfNeeded(JObject args)
{
if (args != null)
{
JObject extra = (JObject)args.GetValue(Constants.KEY_EXTRA);
if (extra != null)
{
bool next = (bool)extra.GetValue(Constants.KEY_NEXT);
if (next)
{
SendUserInputToChatbot(Constants.VALUE_USERINPUT_NEXT);
}
}
}
}
Many of the above explanations have been omitted. Open the solution file of the sample and refer to the Playchat.xaml and PlaychatViewModel.cs files.