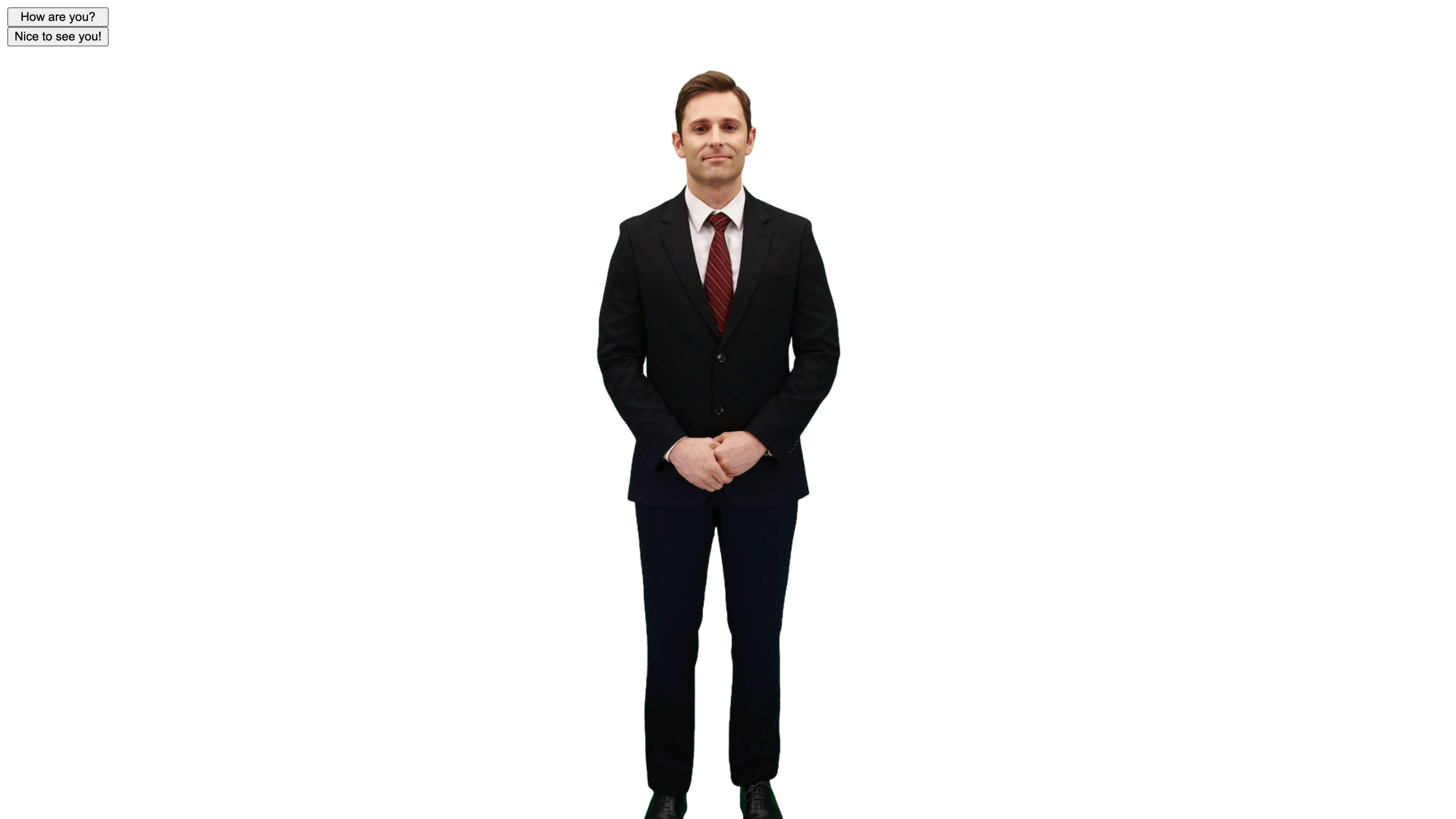
Own your first AI Human
In this chapter, we will quickly set up AIPlayer with the default AI and learn about AI speaking process. When setting up AIPlayer for the first time, it may take several minutes to load depending on the network condition.
1. Including the SDK
Include the JavaScript SDK in the web page as shown below. The URL included in the script is the latest JavaScript SDK download path provided by Deep Brain AI, so you can always use the latest version.
<script src="https://cdn-aihuman.deepbrainai.io/sdk/web/aiPlayer-latest.min.js"></script>
In addition, a specific version other than the latest version may be used as shown below.
<script src="https://cdn-aihuman.deepbrainai.io/sdk/web/aiPlayer-1.4.0.min.js"></script>
2. Specifies the area to contain the AIPlayer object
Designate the HTML Element area to include the AIPlayer object as shown below. You can freely adjust the area where the AIPlayer will be drawn by adjusting the size or position of the area.
<div id="AIPlayerWrapper"></div>
3. Creating an AIPlayer object
Create an AIPlayer object by entering the area where the AIPlayer is to be drawn as an argument to the AIPlayer constructor as shown below.
const wrapper = document.getElementById("AIPlayerWrapper");
const AI_PLAYER = new AIPlayer(wrapper);
4. Authenticating the SDK
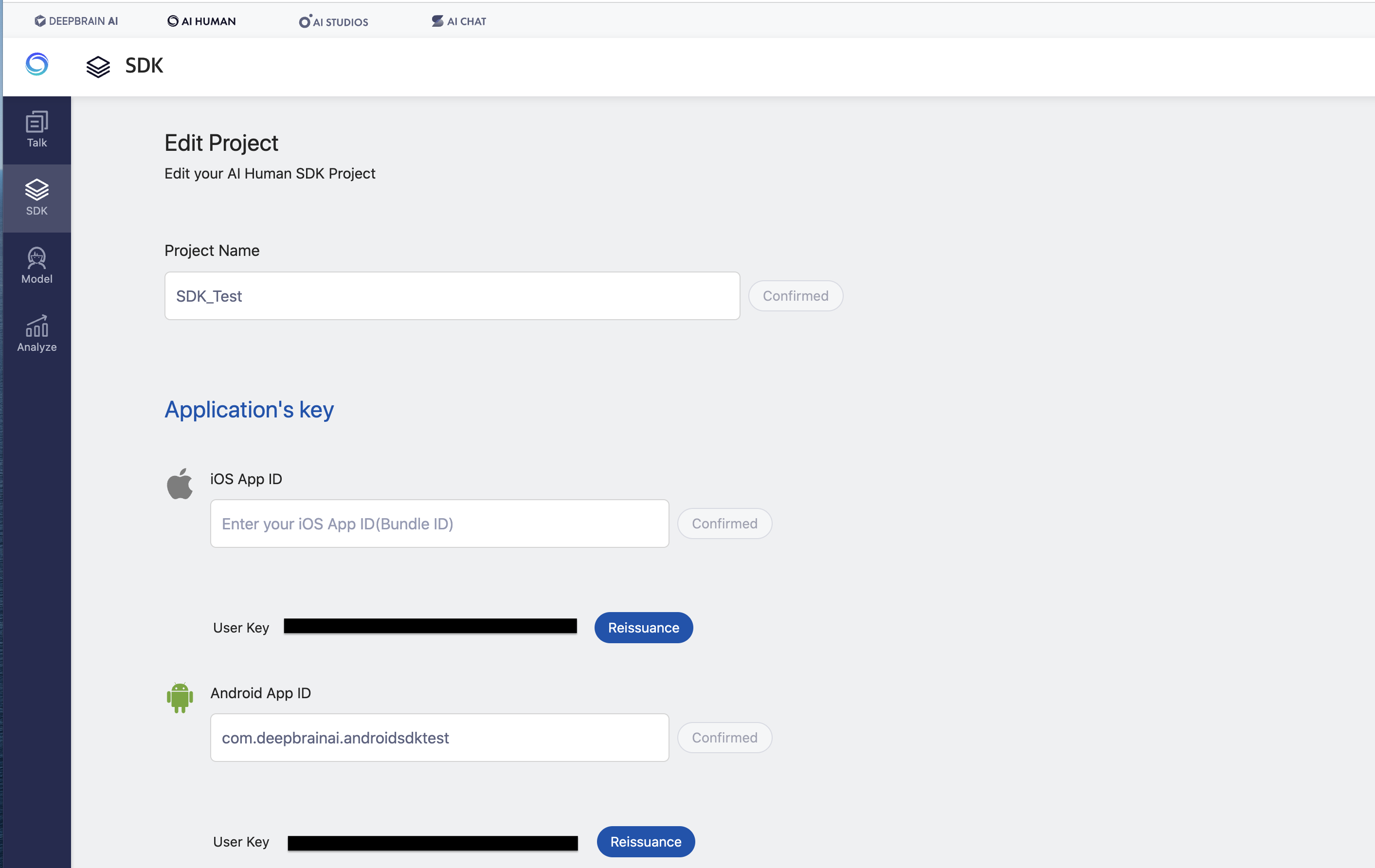
4.1. Setting up appId and issuing userKey on SDK website
- Log in to the SDK website
- If there is no project, you can get a userkey by entering the appId to be used on the web after creation and pressing OK.
- If you have a project, you can check the appId of the project and the userKey issued.
4.2. Create ClientToken on Server
- Next, for SDK authentication procedures, clientToken is created using the JWT library as appId and userKey of the project.
- ClientToken generation is implemented by the server to prevent userKey exposure and is recommended by the client to request and receive.
- Below is an example of installing and generating JWT at npm.(Note: JWT)
npm install jsonwebtoken
- Below is an example of creating a clientToken from a nodejs server to JWT.
// generateJWT.js(Server)
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
const userKey = "..."; // TODO: userKey input
const payload = {
appId: "...", // TODO: appId input
platform: "web"
};
const options = {
header: { typ: "JWT", alg: "HS256" },
expiresIn: 60 * 5 // expire time: 5 mins
};
function generateJWT(req, res) {
try {
const clientToken = jwt.sign(payload, userKey, options);
res.json({ appId: payload.appId, token: clientToken });
} catch (e) {
console.log("jwt generate err ", e.name, e.message);
}
}
- Below is a basic example of routing the generateJWT function in express.
// generateJWT.js(Server) append
module.export = generateJWT;
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const generateJWT = require("..."); // TODO: generateJWT.js access path
app.get('/generateJWT', generateJWT);
// app.post('/generateJWT', generateJWT);
- Below is a basic example of routing the generateJWT function in next.js.
// generateJWT.js(Server) append
export default (req, res) => {
if (req.method === "GET") return generateJWT(req, res);
// if (req.method === "POST") return generateJWT(req, res);
};
4.3. Request generateJWT (clientToken) from Client to Server
// quickStart.js(Client)
async function requestClientToken() {
const result = await makeRequest("GET", "..."); // TODO: Server generateJWT request address input
// Success
DATA.appId = result.appId;
DATA.clientToken = result.token;
// ...
}
4.4. generateToken request
- When the generateToken function is called using appId and clientToken, it responds with JSON containing information such as verifiedToken, tokenExpire, and defaultAI.
// quickStart.js(Client)
async function generateVerifiedToken() {
const result = await AI_PLAYER.generateToken({ appId: DATA.appId, token: DATA.clientToken });
if (result?.succeed) {
DATA.verifiedToken = result.token;
DATA.tokenExpire = result.tokenExpire;
DATA.defaultAI = result.defaultAI;
}
}
5. Initializing AIPlayer
After successful authentication, it is initialized using the init function. At this time, the appId (domain), verifiedToken obtained in the authentication process, and ai_name of defaultAI are used as parameters. If you want to use other AIs, you can get a list of available AIs through the getAIList function. For details, please refer to Main Class API Handbook.
// quickStart.js(Client)
await AI_PLAYER.init({
aiName: DATA.defaultAI.ai_name, zIndex: 0, size: 1.0, left: 0, top: 0, speed: 1.0
});
6. AI Speech (Speaking)
Load the resources required for AIPlayer. After resource loading is completed, you can call send function.
AI_PLAYER.send("Nice to see you!");
7. Full Client Source Code
<!-- quickStart.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>AIPlayer JavaScript SDK Quick Start</title>
</head>
<style>
html, body, #AIPlayerWrapper {
height: 100%;
}
</style>
<body style="height:100%">
<div style="display: none; width: fit-content;" id="AIPlayerTexts">
<button onclick="speak(this.innerHTML)">How are you?</button>
<button onclick="speak(this.innerHTML)">Nice to see you!</button>
</div>
<div id="AIPlayerWrapper"></div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn-aihuman.deepbrainai.io/sdk/web/aiPlayer-latest.min.js"></script>
<script src="./quickStart.js"></script>
</html>
// quickStart.js
const wrapper = document.getElementById("AIPlayerWrapper");
const AI_PLAYER = new AIPlayer(wrapper);
const DATA = {};
initSample();
async function initSample() {
initAIPlayerEvent();
await generateClientToken();
await generateVerifiedToken();
await AI_PLAYER.init({
aiName: DATA.defaultAI.ai_name,
size: 1.0,
left: 0,
top: 0,
speed: 1.0
});
}
async function generateClientToken() {
const result = await makeRequest("GET", "..."); // TODO: Server generateJWT request address input
// Success
DATA.appId = result.appId;
DATA.clientToken = result.token;
// ...
}
async function generateVerifiedToken() {
const result = await AI_PLAYER.generateToken({ appId: DATA.appId, token: DATA.clientToken });
if (result?.succeed) {
DATA.verifiedToken = result.token;
DATA.tokenExpire = result.tokenExpire;
DATA.defaultAI = result.defaultAI;
}
}
function initAIPlayerEvent() {
AI_PLAYER.onAIPlayerStateChanged = function (state) {
if (state === "playerLoadComplete") document.getElementById("AIPlayerTexts").style.display = "grid";
};
}
function speak(text) {
AI_PLAYER.send(text);
}
// sample Server request function
async function makeRequest(method, url, params) {
const options = { method, headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json; charSet=utf-8" } };
if (method === "POST") options.body = JSON.stringify(params || {});
return fetch(url, options)
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => data)
.catch((error) => {
console.error("** An error occurred during the fetch", error);
showPop("Generate Client Token Error", `no client token can be generated.`);
return undefined;
});
}
8. Full Server Source Code
// generateJWT.js(Server)
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
const userKey = "..."; // TODO: userKey input
const payload = {
appId: "...", // TODO: appId input
platform: "web"
};
const options = {
header: { typ: "JWT", alg: "HS256" },
expiresIn: 60 * 5 // expire time: 5 mins
};
function generateJWT(req, res) {
try {
const clientToken = jwt.sign(payload, userKey, options);
res.json({ token: clientToken, appId: payload.appId });
} catch (e) {
console.log("jwt generate err ", e.name, e.message);
}
}
// next.js
export default (req, res) => {
if (req.method === "GET") return generateJWT(req, res);
};
