with AWS Bedrock Claude & AWS Transcribe
- 5.AWS Bedrock Claude & Transcribe
This menu is an example of a Conversational AI service that integrates AI Human, AWS Bedrock Claude and AWS Transcribe. AI Human can be combined with AWS Bedrock Cloud for real-time conversation. Additionally, AWS Transcribe is used to speak like a real person.
Open the 5.AWS Bedrock Cloud & Transcribe scene and try talking to AI. (It can actually work after AWS Transcribe has been set up.) We see that AI recognizes speech and gives appropriate answers through Claude, a large language model of Anthropic. The current demo only consists of text-based conversations, but you can also output images depending on Amazon Bedrock's model or backend settings.

Using AI Human, AWS Bedrock Claude and AWS Transcribe
The aws access information is required to run the interactive AI service mentioned above in the applicable demonstration.
- About Creating AWS Accounts and Accessing : aws-accesskey-id, aws-secret-accesskey, region-endpoint, bedrock-modelid, anthropic-version
Please refer to the page below for an explanation and composition of Amazon Bedrock Claude and AWS Transcribe.
- Getting Started with an Amazon Bedrock-Based Claude: https://aws.amazon.com/ko/bedrock/claude
- Getting Started with Amazon Transcribe : https://aws.amazon.com/ko/transcribe
If you are ready for the AI interactive service, select DemoAWS-Bedrock-Claude-Trancribe in the Hierarchy window of the demo and enter the aws access values prepared above in the Inspector window.
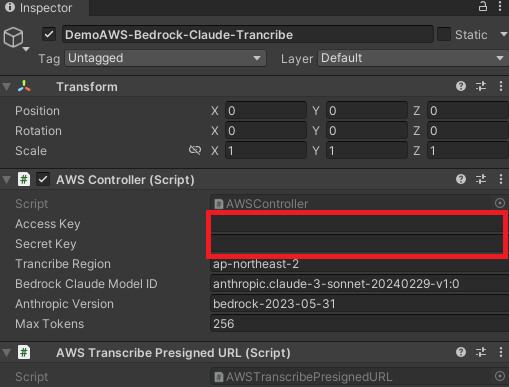
Additionally, RegionEndpoint settings are required for AWS Bedrock Claude connections. In the _bedrockRegionEndPoint variable of the AWSController.cs script, enter the RegionEndpoint value for which the AWS Bedrock service is configured.
// AWSController.cs
readonly RegionEndpoint _bedrockRegionEndPoint = RegionEndpoint.USWest2;
Now you're ready to run the demo. Try talking to AI through the microphone.
Implementing an STT with AWS Transcribe
In this demonstration, AWS Transcribe is linked to convert voice into text.
Create a Presigned URL and try to connect using the Presigned URL via WebSocket. If the connection is successful, send the user voice data via WebSocket via Unity Microphone.
The converted text is available through the WebSocket.OnMessage event.
Below are the main functions of the AWS Controller script for major AWS Transcribe interworking.
// AWSController.cs
// connect websocket
public async void Connect()
{
if (Microphone.devices.Length == 0)
{
Debug.LogError($"{nameof(AWSController)} There are no microphones available.");
return;
}
AWSTranscribePresignedURL transcribePresignedURL = GetComponent<AWSTranscribePresignedURL>();
if (transcribePresignedURL == null)
{
Debug.LogError($"{nameof(AWSController)} Not find the AWSTranscribePresignedURL component.");
return;
}
// get presigned url
string url = transcribePresignedURL.GetRequestURL(_accessKey, _secretKey, _trancribeRegion);
_socket = new WebSocket(url);
int bitRate = Convert.ToInt32(transcribePresignedURL.GetAudioBitRate());
// start microphone
_clip = Microphone.Start("", false, 300, bitRate);
_socket.OnOpen += () =>
{
Debug.Log($"{nameof(AWSController)} Open socket!");
};
_socket.OnError += (e) =>
{
Debug.LogError($"{nameof(AWSController)} Socket Error : {e}");
};
_socket.OnClose += (e) =>
{
Debug.Log($"{nameof(AWSController)} Close socket!");
};
// regist message event
_socket.OnMessage += OnMessage;
await _socket.Connect();
}
// message event
private void OnMessage(byte[] bytes)
{
//First 8 bytes are the prelude with info about header lengths and total length.
byte[] totalByteLengthBytes = new byte[4];
Array.Copy(bytes, totalByteLengthBytes, 4);
if (BitConverter.IsLittleEndian)
Array.Reverse(totalByteLengthBytes);
//an int32 is 4 bytes
int totalByteLength = BitConverter.ToInt32(totalByteLengthBytes, 0);
byte[] headersByteLengthBytes = new byte[4];
Array.Copy(bytes, 4, headersByteLengthBytes, 0, 4);
if (BitConverter.IsLittleEndian)
Array.Reverse(headersByteLengthBytes);
int headersByteLength = BitConverter.ToInt32(headersByteLengthBytes, 0);
//Use the prelude to get the offset of the message.
int offset = headersByteLength + 12;
//Message length is everything but the headers, CRCs, and prelude.
int payloadLength = totalByteLength - (headersByteLength + 16);
byte[] payload = new byte[payloadLength];
Array.Copy(bytes, offset, payload, 0, payloadLength);
string message = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(payload);
AWSTranscribeWebsocketMessage jsonMessage = JsonUtility.FromJson<AWSTranscribeWebsocketMessage>(message);
if (jsonMessage != null && jsonMessage.Transcript.Results.Count > 0)
{
string resultMessage = jsonMessage.Transcript.Results[0].Alternatives[0].Transcript;
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(resultMessage))
{
// display message
DemoAWS demoAWS = GetComponent<DemoAWS>();
if (demoAWS != null)
{
demoAWS.OnMessage(resultMessage, true);
}
// invoke bedrock model
Task.Run(() => InvokeModel(resultMessage));
}
}
}
Implementation of TTS by interlocking AWS Bedrock Claude with AI Human
In this demonstration, AWS Bedrock Claude and AI Human are used to implement real-time conversation capabilities.
First, create the AmazonBedrockRuntimeClient object for AWS Bedrock Claude interworking. (Class objects provided by AWS SDK, and some AWS SDK libraries are included in the AI Human SDK Sample for use in that class)
And set the values required for the request (max_tokens, anthropic_version, etc...) and call Amazon BedrockRuntimeClient.InvokeModelAsync(InvokeModelRequest). The API operates asynchronously and waits for a response.
If the response is normal, order the AI to speak through the AIPlayer.
Below are the main functions of the AWSController script for AWS Bedrock Cloud interworking.
// AWSController.cs
public async Task InvokeModel(string userMessage)
{
if (_bedrockClient == null)
{
_bedrockClient = new AmazonBedrockRuntimeClient(_accessKey, _secretKey, _bedrockRegionEndPoint);
}
var nativeRequest = JsonSerializer.Serialize(new
{
anthropic_version = _anthropicVersion,
max_tokens = _maxTokens,
messages = new[]
{
new { role = "user", content = userMessage }
}
});
var request = new InvokeModelRequest()
{
ModelId = _bedrockClaudeModelID,
Body = new MemoryStream(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(nativeRequest)),
ContentType = "application/json"
};
try
{
var response = await _bedrockClient.InvokeModelAsync(request);
var modelResponse = JsonNode.Parse(response.Body);
var responseText = modelResponse["content"]?[0]?["text"] ?? "";
// Since it is not unity's main thread, we put the response text into a queue and process it in the Update() function.
_reponseClaudeQueue.Enqueue(responseText.ToString());
}
catch (AmazonBedrockRuntimeException e)
{
Debug.LogError($"{nameof(AWSController)} ERROR: Can't invoke '{_bedrockClaudeModelID}'. Reason: {e.Message}");
}
}
private void Update()
{
if (_reponseClaudeQueue.Count > 0)
{
string responseText = _reponseClaudeQueue.Dequeue();
// AI speak
DemoAWS demoAWS = GetComponent<DemoAWS>();
if (demoAWS != null)
{
demoAWS.Speak(responseText.ToString());
}
}
}
The above description is heavily overstated. For more information, see AWS Bedrock Claude & Transcribe Scene in the demo.